What is MCP? How does it compare to API?
阳明
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is a new open protocol designed to standardize how to provide context to large language models (LLMs). You can imagine MCP as the USB-C interface for AI Agents: it provides a unified method for AI Agents to connect to various tools and data sources.
This article will detail the definition, architecture, working principles, advantages and disadvantages of MCP, and compare it with traditional APIs.
What is MCP?
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a standardized protocol for connecting AI agents to various external tools and data sources. Imagine it as a USB-C interface - but for AI applications.
Just like USB-C simplifies the way different devices connect to a computer, MCP simplifies the way AI models interact with data, tools, and services.
Claude MCP is initiated by Anthropic ↗, aiming to make AI models (like Claude) easier to interact with tools and data sources.
But MCP is not just a project from Anthropic, it is open and more and more companies and developers are joining in.
It starts to look like a new standard for AI-tool interaction.
To learn more about Claude MCP, visit claudemcp.com ↗ for more information about the MCP specification and tutorials.
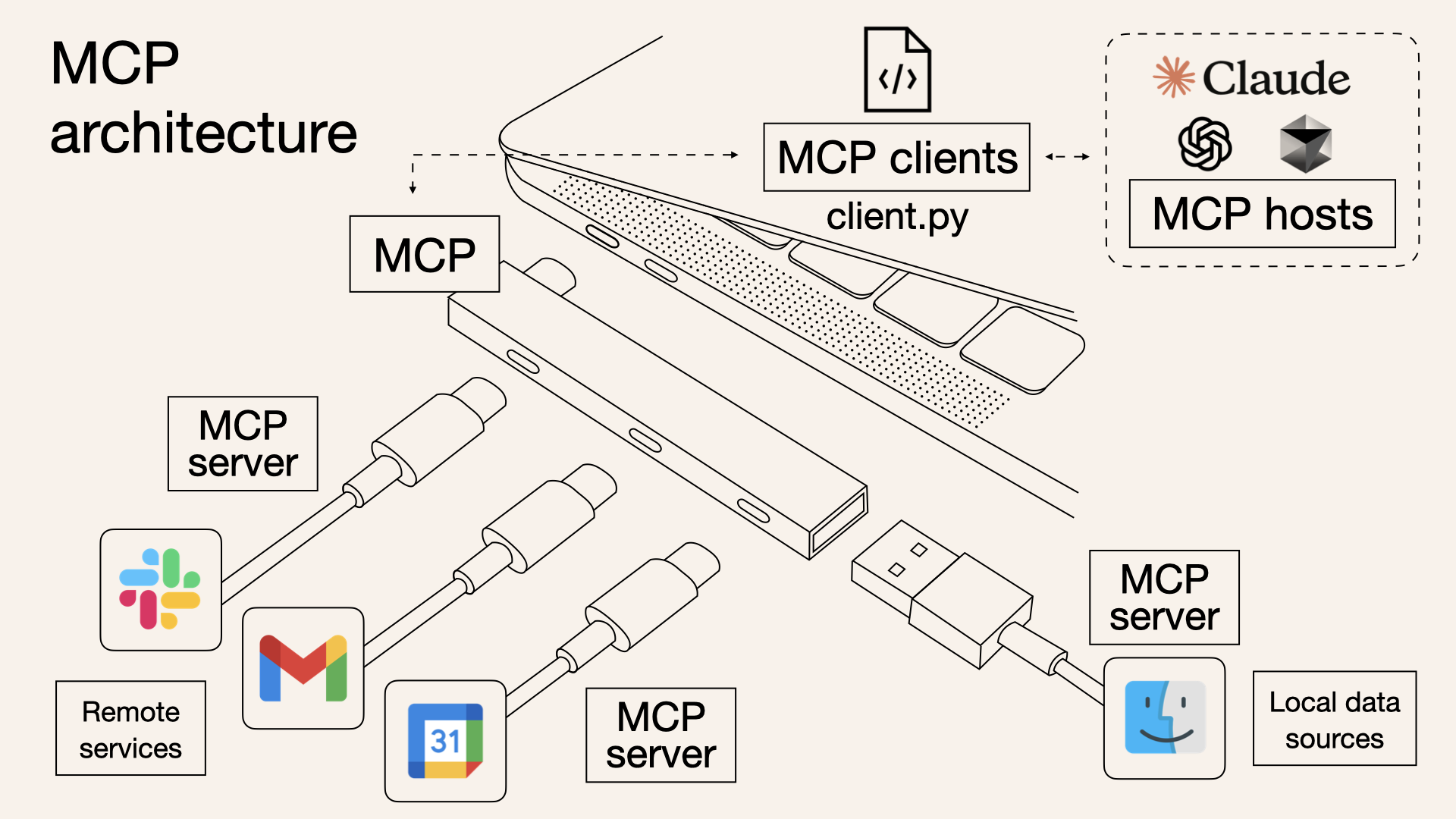
MCP follows a simple client-server architecture:

Image source: https://norahsakal.com/blog/mcp-vs-api-model-context-protocol-explained/
- MCP Hosts: These are applications that need to access external data or tools (like Claude Desktop or AI-driven IDEs)
- MCP Clients: They maintain a dedicated, one-to-one connection with the MCP server
- MCP Servers: Lightweight servers expose specific functionality through MCP, connecting to local or remote data sources
- Local data sources: Files, databases, or services accessed by MCP servers securely
- Remote services: Internet-based APIs or services accessed by MCP servers
Imagine MCP as a bridge, you can clearly see: MCP itself does not handle complex logic; it only coordinates the flow of data and instructions between AI models and tools. Implementing MCP has many benefits:
- Simplified development: Write once, integrate multiple times, no need to rewrite custom code for each integration
- Flexibility: No need to complex reconfiguration when switching AI models or tools
- Real-time response: MCP connections remain active, enabling real-time context updates and interactions
- Security and compliance: Built-in access control and standardized security practices
- Scalability: Easy to add new features as your AI ecosystem grows - just connect another MCP server
Why use MCP instead of traditional APIs?
Traditionally, connecting AI systems to external tools involves integrating multiple APIs. Each API integration means separate code, documentation, authentication methods, error handling, and maintenance.
Traditional APIs are like having separate keys for each door, each door has its own key and rules
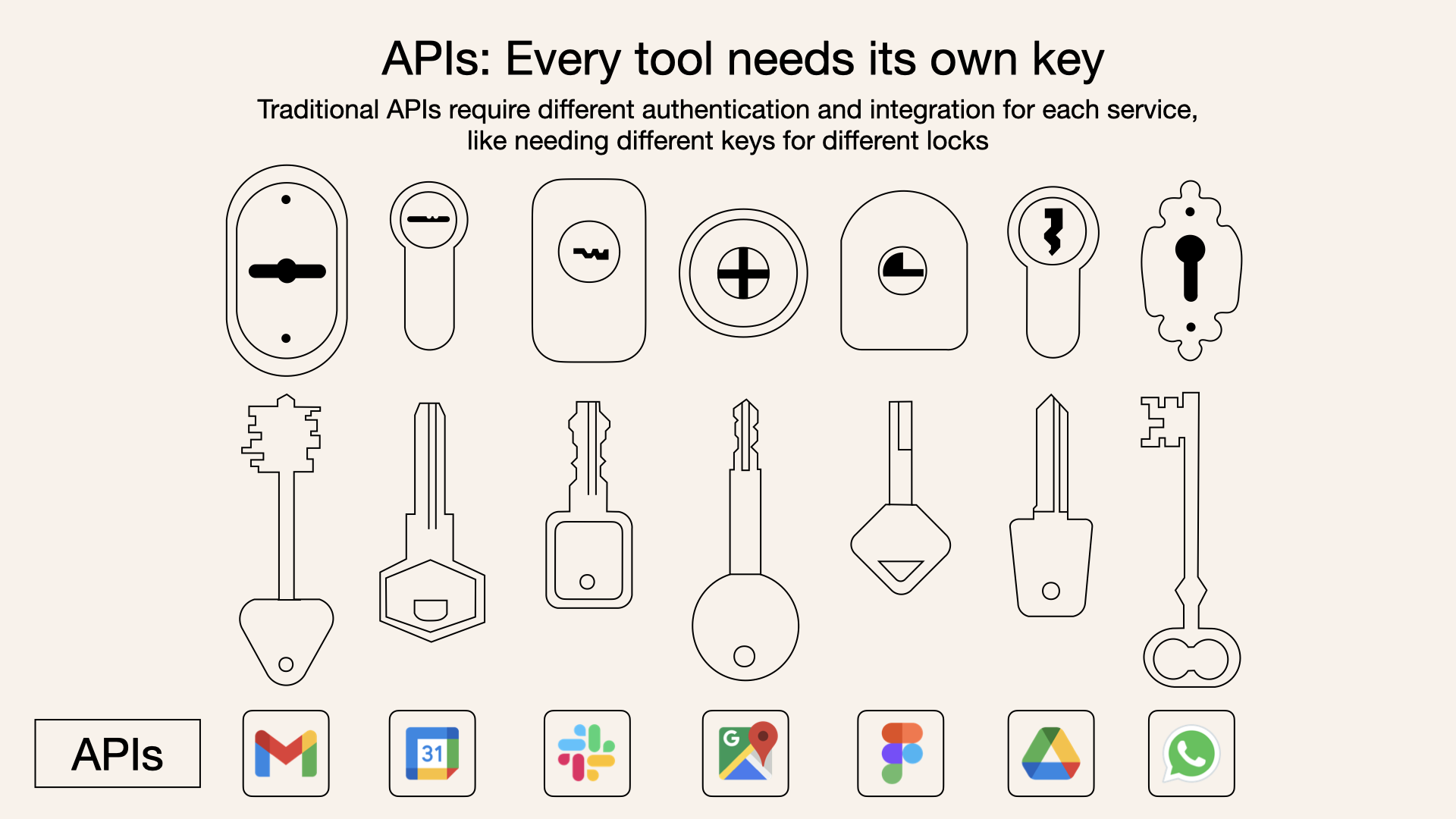
Traditional APIs require developers to write custom integrations for each service or data source, which not only increases complexity but also leads to errors and maintenance issues.
MCP vs API: Quick comparison
| Feature | MCP | Traditional API |
|---|---|---|
| Integration difficulty | Single standardized integration | Separate integration for each API |
| Real-time communication | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Dynamic discovery | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Scalability | Plug and play | Need additional integrations |
| Security and control | Consistent tools | Separate control for each API |
The main differences between MCP and traditional APIs:
- Single protocol: MCP acts as a standardized "connector", so integrating one MCP means potentially accessing multiple tools and services, not just one
- Dynamic discovery: MCP allows AI models to dynamically discover and interact with available tools, without the need for hard-coded knowledge of each integration
- Bidirectional communication: MCP supports persistent real-time bidirectional communication - similar to WebSockets. AI models can dynamically retrieve information and trigger actions
Why is bidirectional communication needed?
- Pull data: LLM queries the server for context → e.g. checking your calendar
- Trigger actions: LLM instructs the server to take action → e.g. reschedule a meeting, send an email
When to use MCP?
Consider these scenarios:
1. Travel planning assistant
- Using API: You need to write separate code for Google Calendar, email, airline booking API, etc., each with custom authentication, context passing, and error handling logic
- Using MCP: Your AI assistant smoothly checks your calendar for availability, books a flight, and sends a confirmation - all through the MCP server, without the need to integrate each tool separately
2. Advanced IDE
- Using API: You need to manually integrate your IDE with the file system, version control, package manager, and documentation
- Using MCP: Your IDE connects to these through a single MCP protocol, achieving richer context awareness and stronger suggestions
3. Complex data analysis
- Using API: You need to manually manage connections to each database and data visualization tool
- Using MCP: Your AI analysis platform discovers and interacts with multiple databases, visualization tools, and simulations through a single unified MCP layer
If your use case requires precise, predictable interactions, and strict limitations, traditional APIs may be more suitable. MCP provides extensive, dynamic capabilities suitable for scenarios that require flexibility and context awareness but are not suitable for highly controlled, deterministic applications.
Summary
MCP provides a unified and standardized way to integrate AI agents and models with external data and tools. It is not just another API; it is a powerful connection framework that makes intelligent, dynamic, and context-rich AI applications possible.
